Can you imagine waking up before sunrise to a day filled with hard labor, instead of going to school with a backpack over your shoulder? It’s hard to imagine, right? But this is the reality of millions of children in India. Child labor robs them of the opportunity to learn, grow, and dream.
With quality education, they will know about their moral rights and can gain knowledge and skills to get a better life. Today we are going to give you a quick overview of the role of education in combating child labor in India, just to make you understand what the main issues are and the challenges usually governing bodies and NGOs usually face while fighting child labor.
The Connection Between Education and Child Labor
Children are the future of India; they must spend their childhood schooling and playing games instead of working in a factory. According to the data, 1 out of 7 children works as a child labourer. The situation is too complex and affected by many factors. Education plays an important role in addressing this problem.
If we go deep into this issue, then we find that poverty is the heart of child labor, there are so many localities where economically deprived families live, and they rely on the income that children bring in from working this act is conveying a wrong message that children must work rather than go to school.
Education helps to protect child’s moral rights, when they attend school, they avoid dangerous jobs and learn about their rights, as they grow, educated are less likely to return to poverty and unsafe work because they have so many better career options.
Also Read:- What Is The Role Of Education In Human Capital Formation?
Factors Contributing to Child Labor
Here are the key reasons why child labor continues to exist:
- Poverty: Many families in India are below the poverty line, and they struggle to fulfil their basic needs. Due to this, they feel the need for their children to work and earn money to support them. In fact, for these families, sending children to school might seem like an expense they can’t afford.
- Lack of Education: Education is not accessible in every area of the country. In some cases where schools are nearby, children are kept at home to work instead of learning because their families believe it’s more important to earn money than to get an education.
- Cultural Beliefs and Social Norms: In some communities, child labor is seen as normal, families expect their children to earn money, and education is always viewed as a priority. In this scenario, cultural beliefs make it harder to change the way people think.
- Weak Enforcement of Laws: India has strict laws over child labor, but they are not always strictly followed, many children work in small factories or on farms, where nobody inspects the place to ensure that children are not being exploited. Hence, child labor continues.
- Lack of Awareness: In some cases, there is a lack of understanding of education, instead of preparing them for schooling, they send them to factories, and they don’t realise that education can lead to better jobs in the future.
- Availability of Cheap Labor: Industries like farming, construction, and textiles mostly hire children because they are paid less than adults. This makes child labor an easy way for businesses to cost-cutting.
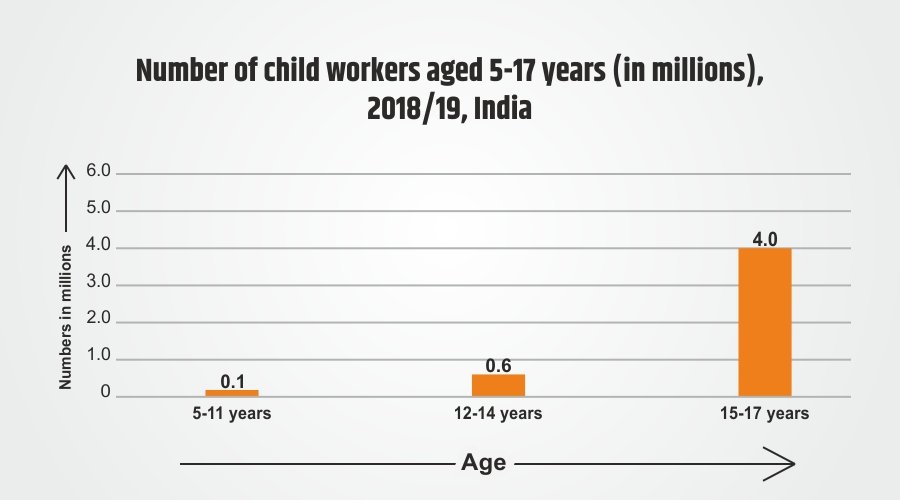
Note: The data mentioned above is of the year 2018-2019
How Education Can Help Combat Child Labor
- Breaking the Cycle of Poverty: Education helps children to learn the necessary skills to run a better life. When they are educated, they can avoid poverty and build a better life for themselves and their families.
- Secure Well-Paying Jobs: Educated individuals are more likely to get better jobs as compared to illiterate ones. It is proven that education can earn you a decent income as an adult.
- Raising Awareness of Rights: Education teaches children about their rights, such as the right to be free from labour and the right to education. With quality education, they are less likely to accept exploitation and become active citizens who can raise their voices for themselves and others.
- Changing Family Mindsets: When children go to school, their parents also realize the value of education, and other people in the neighbourhood also send their children to school instead of sending them to work.
- Increasing Awareness of Child Labor Issues: Education helps children understand the harms, such as health risks and the loss of childhood. As they grow, they can spread this knowledge and help others understand why child labor is dangerous, creating a community effort to stop it.
Government Initiatives and Policies
The Indian government has introduced several programs to reduce child labor and promote education. Here are the key initiatives:
- Right to Education Act (RTE): The RTE Act makes education compulsory for children aged 6 to 14, to support every community of India, the government is providing education free to these children. It makes it illegal for children in this age group to work and aims to get them into school instead.
- Child Labor (Prohibition and Regulation) Act: This law bans the employment of children below age 14 in hazardous jobs and sets rules for non-hazardous work, protecting children from exploitation.
- National Child Labor Project (NCLP): The NCLP helps to save children from work and admit them to special schools for education and skill training.
- Midday Meal Scheme: This scheme provides free meals to government school children; it encourages families to send their children to school while ensuring they get proper nutrition.
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao: This scheme inspires people at the rural level, promotes girls’ education, and aims to reduce child labor among girls by encouraging them to study in school.
- National Policy on Children: The National Policy on Children ensures children’s rights to education, health, and protection, aiming to eliminate child labor by addressing its causes.
- Education for All (EFA): The Education for All program focuses on universal education, especially for children in labor, by making schools accessible and ensuring they stay enrolled.
Challenges and Solutions
Below is the table of the challenges and solutions to child labor in India:
| Challenges | Solutions |
| Poverty | Improving access to education by building more schools, improving infrastructure, and offering free or affordable education. |
| Lack of Awareness | Raising awareness through media, community programs, and local leaders about the importance of education and the dangers of child labor. |
| Inadequate Infrastructure | Providing economic support to families through financial aid or incentives, such as free meals or scholarships. |
| Cultural Beliefs | Strengthening child protection laws by enforcing stricter regulations against child labor and supporting welfare programs. |
| Limited Access for Marginalized Groups | Partnering with local NGOs to offer resources, training programs for parents, and support for at-risk children. Ensuring inclusive education with equal access for all children, particularly marginalised groups, through scholarships and inclusive learning environments. |
Take Away
Education is the first casualty of war, as it is for child labor. It helps children to find better jobs, escape poverty, and stay safe from exploitation. While challenges like poverty and lack of awareness exist, government policies and community efforts can help overcome them.
By making education more accessible, raising awareness, and providing support to families, we can reduce child labor in India. With everyone working together, we can ensure that all children have the chance to go to school and build a brighter future.
FAQs
Q.1 What is child labor in India, and why is it a problem?
Ans:Child labor refers to the employment of children in hazardous or exploitative work, depriving them of childhood and education. India has an estimated 33 million child laborers.
Q.2 What initiatives has the Indian government taken to combat child labor?
Ans:The Indian government has launched initiatives like NCLP, RTE Act, and Child Labor (Prohibition and Regulation) Act to combat child labor.
Q.3 When was child labor banned in India?
Ans:The Child Labor (Prohibition and Regulation) Act was enacted in 1986 and amended in 2017 to completely prohibit child labor below 14 years. The Right to Education Act of 2009 also made education compulsory and free for children between 6-14 years.
Q.4 How can technology be leveraged to promote education and combat child labor in India?
Ans:Technology can be leveraged to promote education and combat child labor in India by providing online educational resources, promoting digital literacy, and supporting advocacy efforts to combat child labor.
Q. 5 What is the role of the government in preventing child labor?
Ans:Enforcement of laws, awareness campaigns, and education programs.