The New Education Policy 2024 (NEP 2024) marks a significant shift in India’s educational landscape, aiming to revolutionize learning from foundational to higher levels. They underline integrated approaches to learning, providing opportunities for personal and academic skills enhancement and curriculum openness. This policy highlights the issues of fairness, the use of technologies in the learning processes to improve its results and the development of thinking and creative skills. Being a Vocational Education and Training institution with learner-centeredness as its philosophy, it is dedicated to preparing its students for the world of the 21st century and transforming the face of India into a knowledge society with innovation and inclusiveness as the pillars of growth.
What is the New Education Policy 2024 (NEP)?
The New Education Policy 2024 lays down the new direction for Indian education, which is flexibility, integration, and learner experience. It is to strengthen the key comprehensive competencies of reading, writing, and numbers, implying critical analysis, creativity, and digital skills in the course of primary education. It recommends that the schooling structure should be a 5+3+3+4 structure, doing away with the previous 10+2 structure relating to preschool to secondary reforms. It promotes vocation-based learning and teaching and training, transactions and progression through the systems of higher education and technology. The policy aims at efficiency, equality, quality, and development, as well as seeking conformity to international standards to produce wholesome persons for a knowledge-based society.
Also Read:- Online MBA Courses
History of the New Education Policy
- 1968: The First National Policy on Education was formulated in 1966, which stressed Compulsory Education and Regional Languages.
- 1986: NPE that provided for provisions of inclusion and improvement of infrastructure through Operation Blackboard and Mid-Day Meal Scheme.
- 1992: Narrowed down the meaning of NPE to resolve the new challenges and incorporate training of teachers as well.
- 2015: T. S. R. Subramanian's committee constituted a new policy and submitted a report in 2016.
- 2017: K. Kasturirangan committee framed the new policy.
- 2019: The proposal for the New Education Policy, or NEP, has been released for the public to give their opinions on it.
- 2020: The education minister signed NEP 2020, which contained a lot of new changes.
- 2023-2024 : Continued implementation and updates.
Key objectives of the National Policy on Education
- Education must be provided to all children so that they can avail themselves of quality education irrespective of their social and economic status.
- Improving the learners’ outcomes by increasing the efficiency of teaching, methods, and knowledge through curriculum improvement, faculty and staff training and improvement, and construction of learning environments.
- To increase the employability skills of the learners, vocational education should be incorporated into the main schooling system.
- Special provisions for the educational improvement of the disadvantaged and the marginalized sections of society.
- Promotion of Languages: Trying to sustain and enhance multilingualism by urging the usage of local language or first language as a way of transmitting lessons.
- Support and encourage research for innovation in education to solve problems within society and advance the sustainable development of society.
Why do we need a New National Education Policy 2024?
A new National Education Policy (NEP) is essential to address the evolving educational landscape and to align India’s education system with global standards and future challenges. The previous policies, developed many years ago, were so ineffective in addressing the issues of an emerging society that is bounded by technological innovation, global competition, and different learning requirements.
The NEP also seeks to bring into practice measures that are created to balanced development, reasoning, and innovation among the learners right from their tender age. It is a character focus on initial literacy, numeration, and the combination of the learning processes to prepare learners for the competent vocational activities basically forms of the 21st century. Furthermore, the policy also focuses on the principle of participation; this is mainly about provisions for quality education for children in marginalized societies.
Structural Changes in School Education
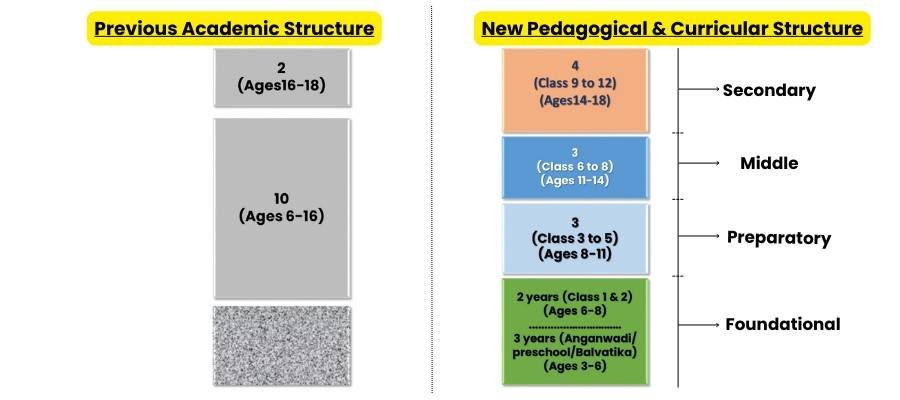
Introduction of 5+3+3+4 Structure 2024
1. Foundational Stage (Ages 3-8):
- This stage includes the early years of schooling and is also referred to as the primary schooling stage, which is the first five years of school.
- This defines it as the first three years of non-formal education – Anganwadi or pre-school and the initial two years of primary education (grades 1-2).
- Focuses on play-based and activity-based learning because children learn better when they are actively involved.
- Teachers are trained in how to enroll the main goal of developing natural curiosity and creativity together with the basic skills among the given children.
2. Preparatory Stage (Ages 8-11):
- The following three years, the 3-5, belongs to the preparatory level.
- Contributes to the process of gradually constructing the student based on skills acquired at the previous stage.
- Introduces experiential learning methods, using themes for enhanced knowledge and critical abilities.
- Curriculum includes subjects that integrate arts, humanities, sciences, and vocational skills to provide a well-rounded education.
3. Middle Stage (Ages 11-14):
- Grades 6-8 is the middle stage of schooling.
- Focuses on subject-specific learning and continues the emphasis placed on pupils’ holistic development.
- Encourages students to learn about various topics and how the different concepts within a subject are formulated through inquiries.
- Provides flexibility in subjects to take and encourages the integration of different fields of study.
4. Secondary Stage (Ages 14-18):
- The secondary stage is the final four years of schooling, grades 9-12.
- Prepares students for higher education, vocational training, or employment.
- Enables students to choose subjects, possibly the careers and interests they may have in mind.
- Emphasizes skill development, critical thinking, and application-oriented learning to enhance employability and adaptability.
Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE)
Importance of Early Education
Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) is really important because it’s the beginning of a child’s learning journey. From birth to about eight years old, kids grow and learn very quickly. This time is crucial because what they experience and learn early on sets the stage for the rest of their lives.
- Learning Skills: Education is beneficial since it enables children to learn basic skills such as reading, writing, and counting. It educates them on how to think and solve problems, and these are skills you will find very useful in school and in life.
- Social Skills: It’s not just about academics. Early education also teaches kids how to get along with others, share, and take turns. These social skills are essential in making friends and being able to cooperate with other people in the later years.
- Health and Well-being: Kids who are in early education are taught issues related to health, food, and their bodies. This makes them grow up to be strong and healthy women.
- Fair Start: ECCE gives every child a fair start. They may not be brought up in similar circumstances, and they may not be equally smart or skilled, but early education allows kids to learn in a group.
Proposed Changes in ECCE
Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) is really important because it’s the beginning of a child’s learning journey. From birth to about eight years old, kids grow and learn very quickly. This time is crucial because what they experience and learn early on sets the stage for the rest of their lives.
- More Places to Learn: The government sees that each child has a centre in which he or she can learn, play, or develop. Obviously, this might imply the construction of more preschools or the enhancement of available preschools.
- Better Teachers: The people who teach young kids need special training. Since the government is involved in the practice of early education programs, it would wish to ensure that teachers in early education programs understand how to assist children in learning and developing optimally.
- Playing and Learning Together: The best method for kids, especially when teaching them something new, is when they are engaged in playful activities. The new plan wishes to be confident that a child will have adequate time to play, learn and acquire new knowledge each day.
- Parents and Families: Families are really important in a child’s learning journey. This new plan aims to enable parents to begin to understand how they can assist their children back home and be involved in their learning.
- Making it Fun: Learning should be fun! The new plan is designed to incorporate games, stories, and fun activities to teach car and Sylvan children.
Higher Education Reforms
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Encourages students to study subjects across different fields to get a broad education that enhances problem-solving and innovation.
- Establishment of MERUs: Introduces multidisciplinary education and research universities (MERUs) to implement interdisciplinary facilities and advance research. These institutions target linking interdisciplinary and offer a forum for interdisciplinary research.
- Flexibility in Course Choices: Offers students the freedom to choose from a wide range of courses across disciplines. This flexibility enables them to design their learning to suit their preferences and career aspirations, hence the concept of student-centred learning.
Vocational Education and Skill Development
Integration of Vocational Education at All Levels:
- In the National Education Policy (NEP), there is a provision for including vocational education for students starting from school-going children.
- Schools will provide vocational education together with academic education, making education more practical rather than theoretical.
- Vocational education will be designed to meet industry needs, preparing students for employment and entrepreneurship.
Skill Development Initiatives:
- NEP aims at skill development and the strengthening of its various activities like apprenticeships, internships, and vocational training.
- It promotes partnerships between education providers, employers, and skills development stakeholders to ensure cohesiveness and credibility of the skills development process.
- The focus is on core skills that are vital in fields such as verbal and written communication, analyzing and solving problems, and computer knowledge.
- Openness to continual education and professional development will be offered to students and other professionals to meet emerging industry needs.
Teacher Education and Training
Continuous Professional Development
- The National Education Policy (NEP) also focuses on lifelong learning and Professional Development (PD) or Continuing Professional Development (CPD) of teachers.
- The CPD programs aim to enhance teaching skills, knowledge in content areas, and the use of technology in instruction.
- Teachers will have opportunities for workshops, seminars, online courses, and mentorship to enhance their teaching practices and stay updated with educational advancements.
New Standards for Teacher Education
- NEP puts new standards for teacher education programs as a way of enhancing the quality of the programs offered.
- Special attention is paid to the strict requirements for entering a university, including the tests checking subject knowledge and the ability to teach.
- Teacher training programs will involve useful classroom exposure and academic learning to adequately equip educators.
- Specializations in areas like inclusive education, digital literacy, and child psychology will be incorporated to address diverse educational needs.
Use of Technology in Education in NEP 2024
Digital Infrastructure and Tools
- According to NEP, the establishment and development of robust digital infrastructure in schools and educational institutions is a high priority.
- This includes ensuring high-speed internet connectivity, access to digital devices, and availability of educational software and tools.
- Teachers shall also be prepared with smart technologies that will replace blackboards, and students shall be accorded multimedia equipment in their schools.
Online and Blended Learning Models
- NEP encourages the utilization of the Internet and other technological approaches so that learning delivery would be more elastic.
- Online learning allows students to access educational content remotely; they can learn based on their timetable while receiving one-on-one instructions.
- Blended learning combines online and face-to-face instruction, offering a balanced approach that combines technology with traditional teaching methods.
- Teachers and learners will have to undergo professional development in the use of technologies for delivering and participating in effective and fun lessons and activities.
Promoting Regional Languages
- Multilingualism in Education: NEP advocates for the involvement of the flexible language policy that is supportive of the multilingual approach as one of the strategic frameworks for the implementation of educational practice. It promotes the inter- and intra-state languages side by side with Hindi and English in all the phases of schooling, thus enabling students to learn cultural and linguistic diversity.
- Curriculum Integration: regional languages and even dialects are assimilated into the curriculum to make sure they are passed from generation to generation for educational purposes. This comprises presenting the subjects and learning materials as well as administrative matters in regional languages, which assist students in learning in their mother language besides gaining proficiency in other languages.
- Teacher Training and Capacity Building: Teachers skilled in regional languages are being trained, as stated by NEP, which is further aimed at improving teachers’ skills to deliver relevant language and teaching competencies. Thus, human development maintains inclusion education practices and enhances the educational context for learners with multiple language profiles.
- Cultural Preservation: By supporting regional languages and dialects, NEP is attempting to safeguard and promote regional languages and dialects as part of India’s pluralistic cultural fabric. It acknowledges languages as important tools of cultural and identity communication domain, which fosters national cohesion while recognizing linguistic regionalism.
Inclusion and Equity
- Targeted Support Programs: NEP proposes targeted interventions and support programs aimed at marginalized communities, including scheduled castes (SCs), scheduled tribes (STs), and economically weaker sections (EWS). This involves scholarship programs, financial aid, and other special arrangements to improve the Intention of education.
- Affirmative Action: Regarding minorities, the policy recommends affirmative action to ensure that minorities get a chance to get to school. This encompasses the issue of quotas and reserves in admissions, employment of faculty and other staff, and other leadership positions for the purpose of increasing the proportion of those who will benefit from the services.
- Inclusive Education Practices: NEP promotes inclusive education practices that accommodate diverse learning needs and backgrounds. Adaptability in learning institutions and effective teaching methodologies in schools should be provided for children with disabilities and other exceptional kids.
- Community Engagement: NEP provides a special focus on social and economic engagement and partnership to remove hindrances in the education sector. It also promotes cooperation between schools, LA, and other community agencies to increase awareness, demand, and supply of support for the development of the target population.
Governance and Regulation
- Central Regulatory Body: NEP proposes the establishment of a single, overarching regulatory authority for higher education, the Higher Education Commission of India (HECI). HECI will eliminate traditional regulatory agencies such as the University Grants Commission (UGC) and ensure the quality, openness, and independence of each institution for higher learning.
- State and Local Governance: The policy emphasizes decentralization and greater autonomy for states and local bodies in managing education. It makes states implement national policies in a way that meets local needs and, at the same time, follows standard education requirements.
- Role of Educational Bodies: Several organizations, such as the National Council of Educational Research and Training ( NCERT) and State Councils of Educational Research and Training (SCERTs), are important institutions under NEP. These ministries are responsible for designing and implementing curriculums, training teachers, and conducting research on education processes and achievements at the national level with regard to the regional necessities of education.
- Quality Assurance: NEP also promotes of quality assurance mechanisms in various levels of education. This recognizes accreditation agencies and the regulatory authorities’ responsibility to enforce the enhancements of the inn and strive to further advance educational quality.
Financing Education
- Increased Public Investment: NEP advocates for raising the public expenditure on education to 6 per cent of the nation’s GDP, and a portion of it has to be spent on imparting ECCE and foundational learning where provisions need to be made for equalizing inequalities in coverage and quality. Extra funding is necessary to strengthen basic facilities, upgrade the quality of the education profession, and increase students’ academic achievements at all levels of education.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: NEP also has provisions for budgetary reform and rational use of the country’s available resources. It supports outcome-based budgeting for integrating a relevancy apparatus that targets the financial resource toward an agenda similar to constructions and formations, digital competencies, and research and learning in education.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): The policy encourages partnerships between government agencies, private sector entities, and non-profit organizations to leverage additional resources and expertise in education. This includes partnerships in building infrastructure, technology, and skills training for improving the quality of education and students’ enrollment.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: NEP emphasizes robust monitoring and evaluation mechanisms to assess the impact of financial investments. It promotes transparency and accountability of funds used in the enhancement of education, and priority is given to an annual assessment of the funds’ usage to identify areas for improvement in education results.
Challenges of NEP 2023
- Implementation Issues: Implementing policy across this framework at the state level and across regions with differing abilities and capacities.
- Infrastructure Development: The limitations include inadequate facilities such as physical spaces, classrooms, laboratories, and even connections to the Internet as a way of learning.
- Teacher Training: Making sure that all teachers, whichever the zone, understand the new curriculum taught and teaching methods in NEP 2023.
- Assessment Reforms: Creating more objective ways of assessing the information that focuses on new learning outcomes, avoiding the excessive use of dichotomous knowledge tests and checklists.
- Equity Concerns: Solving the issues of inequality in access to quality education between the centre and provinces and between the rich and the poor.
- Curriculum Overhaul: Introducing new subjects and skills into the curriculum and incorporating them into the curriculum, particularly the new skills in an area such as coding or vocational skills, without forgetting core academics.
- Budget Allocation: Acquiring sufficient capital and funding to implement adequate resources in order to achieve the proposed plan of NEP 2023.
- Stakeholder Engagement: This involves support and cooperation from most of the stakeholders in society, such as teachers, parents, and educational entities.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Laying down sound procedures that would be used in the assessment of progress, assessment of the outcomes, and responses to action to the gaps found in order to get the intended results.
Summary
The National Education Policy (NEP) is a policy measure that has been proposed to make all-round changes with the intention of revamping the educational system in India. As a result of focusing on the principles of inclusiveness, quality, and flexibility, NEP attempts to balance learners’ needs, optimize general development and enable learners to thrive in the constantly changing world. As such, its multilingualism interest, equal chances, and the call for higher public spending resonate with combating past issues while advocating for radical change in the provision of education. NEP 2023 aims to build teachers’ capacity, improve educational processes, and position India as a knowledge power, thereby developing the structural framework and guidelines for the education system.
FAQ
1. What are the main goals of NEP 2023?
The main strategic objectives of NEP 2023 are to produce global citizens for the students, social equity and inclusion for the students and use of technology in education.
2. How will NEP 2023 change school education?
NEP 2023 will restructure school education into a 5+3+3+4 model, emphasize on learners’ critical thinking abilities and creativity, as well as implement the competency-based assessment.
3. What reforms are proposed for higher education under NEP 2023?
Higher education reforms include multiple discipline education and training, formation of Multidisciplinary Education and Research University, and diversified elective courses.
4. How will NEP 2024 impact teachers?
NEP 2024 therefore focuses on the professionalism of teachers, the use of information and communication technologies in instruction and the reduction of student-teacher ratio to enhance learning.
5. What is the role of technology in NEP 2023?
Another important aspect of NEP 2023 is technology-related, and it is focused on promoting digital academic infrastructure, online and distance learning formats, and the creation of the National Educational Technology Forum (NETF).